Learn different methods to check if a value is NaN in Python, using libraries like pandas, numpy, and the math module, with practical examples and code snippets.
What is a NaN Value?
NaN stands for “Not a Number”. In Python, A NaN is a special value that shows up when either a number is missing, or the calculations don’t make sense. For example, if you divide a value by 0, the result is undefined and Python might return a NaN. Taking the square root of a negative number can also result in a NaN value. When working with data in Python, there are situations where you might need to represent missing or undefined values. In such cases, Python provides a special way to define NaN by using float('nan').
Difference Between Nan, Zero, and Null Values
When understanding the concept of NaN values, people often gets confused between NaN, zero and empty values. Here are some key differences between them which will make sure that you don’t get confused.
NaN
In Python, NaN represents data that is either missing or not defined. It is used when a calculation doesn’t produce a valid result or when some data is unavailable. For example, dividing any number by zero would result in NaN.
Zero
The number zero, shown as 0, is a valid value that is used to represent no quantity of something. It is not the same as NaN, as zero is still a valid number, while NaN shows that a value is missing or invalid.
Null
NULL means no value or empty. It is different from NaN and zero as it shows that there is nothing at all in that place. It is just like an empty box where no data has been put yet.
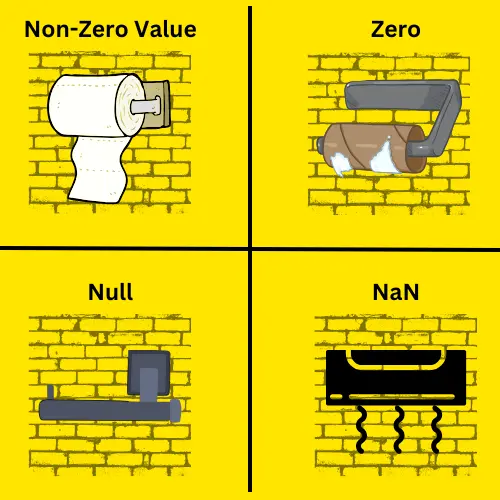
Real World Analogy
Imagine you’re visiting a building with four washrooms. In the first washroom, the toilet paper holder is full. This represents a non-zero value because there’s a valid, usable amount. In the second washroom, there’s an empty roll on the holder, representing zero. The holder exists, but there’s nothing usable on it. In the third washroom, the holder itself is missing. It represents null as no data is assigned at all. Finally, in the fourth washroom, Instead of a toilet paper holder, there’s a hand dryer. This represents NaN. The data type or context is completely unexpected.
Ways To Check if a Value Is NaN in Python
In Python, there are multiple methods to check if a value is NaN. We will explore each of these concepts through code, real-world examples, and simple visual comparisons.
Using numpy Library
The easiest way to check if a value is NaN is by using the numpy library. This library has a function called isnan() which is used to identify Nan values in a data. Keep in mind that the isnan() function of numpy library only works on numerical numbers such as floating point numbers and arrays that contains numeric data.
Syntax
import numpy numpy.isnan(value)
Import numpyimports the numpy library.numpy.isnan(value)calls theisnan()function ofnumpymodule and passes the value to it as a parameter to checks if the value is a NaN value.
Example Code
In this example code, first the numpy module is imported. Then a value with NaN is declared. In if condition, the isnan() function of numpy module is used by placing a dot ‘.’ Operator after the numpy module to check if the value is a NaN. If the value is a NaN, then the print statement will print that the value is NaN, else it will print that the value is not a NaN.
import numpy
value = float('nan')
if numpy.isnan(value):
print("The value is NaN")
else:
print("The value is not NaN")Output
The value is NaN
Using panda Library
The pandas library have the isna() function which can be used to check if a value is NaN. The isna() function takes a variable as a parameter and returns true if the variable have a NaN value, otherwise it return false. The numpy.isnan() only works on numerical datatypes while pandas.isna() works on any data type, including numerical, strings, objects, and even entire Pandas Series or DataFrames (data in form of table).
Syntax
Import pandas pandas.isna(value)
import pandasimports the pandas library.pandas.isna(value)calls theisna()function of pandas library and passes the value to it.
Example Code
In this code, the pandas library is first imported. Then a variable is declared with a NaN value. The isna() function from the pandas library is called by using the dot operator after the library name, and the variable is passed to it. Finally, a print statement is used to display the value returned by the isna() function.
import pandas
value = float('nan')
print(pandas.isna(value))Output
True
Importing math Module
In Python, the math module is a standard built-in module that provides mathematical functions which are useful for various mathematical operations. The math module provides a function called isnan() which works similarly to the isnan() function of the numpy library but on a bit lower level.
You can use the isnan() function of the math module to check if a value is NaN by passing the value to it as a parameter. However, using this function, you can only check if a single value is NaN and it only works on numerical values.
Syntax
import math math.isnan(value)
import mathimports the math modulemath.isnan(value)calls theisnan()function of math module and passes value to it as a parameter to check if the value is NaN.
Example Code
First, the math module is imported in this code. Then, a variable is created and assigned a NaN value. The variable is then passed to the isnan() function of the math module and a print statement is used to print the value returned by the function.
import math
value1 = float('nan')
print(math.isnan(value1))Output
True
Using float(‘nan’) Comparison
In Python, NaN is considered unequal to any value, including itself. This means a NaN value is never equal to itself. You can use an if condition to compare a value with itself. If the value is equal to itself, then it is not a NaN value, otherwise, it is a NaN value.
Example Code
In this code a variable is declared with NaN value and then it is compared with itself. If the value is a NaN value, then it can’t be compared with itself and will return false.
value = float('nan')
if value != value:
print("The value is NaN")Output
The value is NaN
Finding a NaN value in an array
You can check for NaN values in an array or a list using pandas.isna(), numpy.isnan() or math.isnan(). However, the math.isnan() function cannot handle arrays directly as it only works on single numeric values.
Using A for Loop To Check Each Element of Array
You can use the math.isnan() in a for loop to check if the array contains any NaN values. The for loop will iterate over each element in a list or array, checking one by one if the value is NaN.
Syntax
import math
for value in array:
if math.isnan(value):
print("Found Nan")import mathimports the math module.for value in arrayloop goes through each item in the array, one by one.if math.isnan(value)check if the element of the array is a NaN.printstatement is used to print that a NaN value is found when the if statement is true.
Example Code
This code starts by importing the math module. Next, an array is created with a NaN value placed in the middle. A for loop then goes through each item in the array to check if it is NaN.
import math
values = [1, 2, float('nan'), 4, 5]
for value in values:
if math.isnan(value):
print("Found NaN")Output
Found NaN
Directly Checking an Array for NaN Values
In Python, the pandas.isna() function and numpy.isnan() function works in a similar way when you are working with numerical arrays. You can find all the NaN values in an array, by passing it to either the pandas.isna() function or numpy.isnan() function. The function will return an array with True values on indeces where NaN was found and False values on indeces where NaN was not found.
Syntax
Import pandas pandas.isna(array)
import pandasimports thepandaslibrarypandas.isna(array)calls theisna()function ofpandaslibrary and passes the array to it.
Example Code
In this code, first the pandas library is imported. Then an array is initialized which contains one NaN value. The isna() function of pandas library is called and the array is passed to it. The isna() function will return an array with True and False values, which is stored in result and then the result is printed using the print statement.
import pandas
array = [1, 2, float('nan'), 4, 5]
result = pandas.isna(array)
print(result)Output
[False False True False False]
Checking for NaN in a DataFrame
In Python, a DataFrame is a two-dimensional structure similar to a table with rows and columns. It can hold different types of data, like integers, floats, and strings. To find the NaN values in a DataFrame, you can use the isna() function of the pandas library by passing the DataFrame to it. The function will return a data set with True values in places where NaN is found and False values in places where NaN is not found.
Syntax
import pandas pandas.isna(dataframe)
import pandasimports thepandaslibrarypandas.isna(dataframe)calls theisna()function ofpandaslibrary and passes the dataframe to it to check for any NaN values.
Example Code
In this code, first the pandas library is imported. Then a pandas DataFrame is created which contains one NaN value. The DataFrame is passed to the pandas.isna() function and finally, a print statement is used to print the value return by the function.
import pandas
data = {'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Jack'], 'Score': [85, float('nan'), 90]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data)
print(pandas.isna(df))Output
Name Score 0 False False 1 False True 2 False False
Comparison Table
The following table lists the main difference between all the methods discussed in this article:
| Feature | numpy.isnan() | pandas.isna() | math.isnan() | value != value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Library | numpy | pandas | math | None (built-in) |
| Handles Single Value | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Handles Arrays/List | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Handles DataFrames | No | Yes | No | No |
| Example Function Call | numpy.isnan(val) | pandas.isna(val) | math.isnan(val) | value != value |
Conclusion
In Python, we can check if a value is nan using different methods from libraries like numpy, pandas, and math. Each method has a specific purpose, depending on the data type you’re working with. The numpy library is great for handling numerical arrays, pandas library is great for handling arrays,list and DataFrames while the math module is simple and built into Python for checking individual values.
FAQs
What is NaN in Python?
NaN stands for “Not a Number”. It represents missing or undefined data, like when a mathematical operation fails such as dividing a number by zero.
How do I find out if a value is NaN?
You can use libraries like numpy, pandas, and math, or compare a value to itself (since NaN is not equal to itself).
What is the difference between NaN, zero, and null?
NaN means missing or undefined data, zero is a valid number representing no quantity, and null means there is no value at all.
Can I check NaN values in a list or array?
Yes, you can use numpy.isnan(), pandas.isna(), or a for loop with math.isnan() to check for NaN values in arrays.
Is it necessary to install numpy or pandas to check for NaN?
No, you can use the built-in math module, but libraries like numpy and pandas offer more powerful features for handling NaN values in arrays and DataFrames.

