Cloud computing is evolving everywhere, and 2024 is the perfect time to turn innovative ideas into businesses. With its flexibility and low startup costs, the cloud opens doors for solutions that make life easier, data smarter, and businesses more profitable.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or an entrepreneur, this list of cloud computing business ideas will help you spot opportunities and take the first step toward building something impactful.
- What is Cloud Computing?
- The Origin of Cloud Computing
- Why is Everyone Turning to Cloud Computing?
- Categories for Cloud Computing
- Top Cloud-Based Ideas to Chase
- Gaming as a Service (GaaS)
- Cloud-Powered Telemedicine Platform
- Energy-optimized Cloud Computing
- DevOps Automation and Infrastructure-as-Code
- Edge Computing and IoT Integration
- Virtual Reality (VR) Therapy
- Real-Time Translation Services
- Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS)
- Cloud Cybersecurity
- FinOps for Cloud Cost Management
- Conclusion
What is Cloud Computing?
Imagine using electricity from a grid instead of running your own power plant. Cloud computing works similarly. Instead of owning costly hardware or software, you access computing power, storage, and applications through the internet from remote data centres.
In simpler terms, cloud computing is like a shared virtual workspace. It lets you perform tasks, store data, and use tools without managing the physical resources yourself.
You might already be using cloud computing without realizing it:
- Saving photos on Google Drive instead of your phone? That’s cloud storage in action.
- Streaming movies on Netflix? The content is delivered from cloud servers, not DVDs or your local device.
The Origin of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has existed since the 1960s when John McCarthy, a computer scientist, introduced the idea of “utility computing,” imagining a future where computing services could be shared like water or electricity.
This idea slowly evolved over the years. By the early 2000s, faster internet speeds and large data centres built by companies like Amazon and Google made cloud computing a reality. These data centres allowed people to access computing power and storage online whenever they needed it without buying or managing physical equipment.

Why is Everyone Turning to Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing has changed how businesses and individuals use technology by making it more accessible and flexible by providing as follows:
- Cost Savings: You don’t need to buy expensive hardware or spend on maintenance.
- Accessibility: Access your tools and data anytime, from any location.
- Scalability: Increase or decrease resources based on what you need.
- Automatic Updates: Get the latest software and security updates automatically.
- Collaboration: Work with your team in real-time, no matter where they are.
- Data Security and Recovery: Cloud services protect and help recover your data if something goes wrong.
- Environmental Impact: Shared resources reduce energy use and waste.
- Innovation: Use advanced tools without managing complicated systems yourself.
Categories for Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing can be categorized into three parts, which include the following:
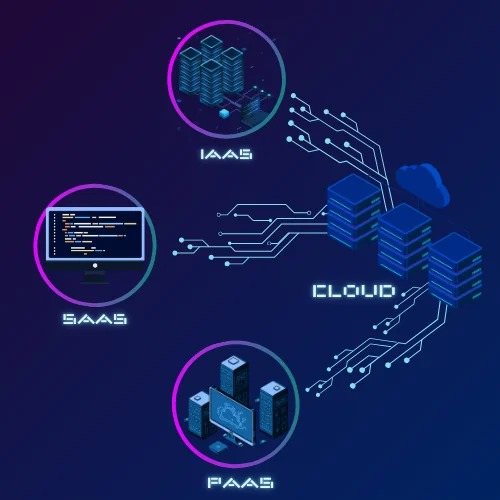
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides an online IT infrastructure like servers, storage, and networking over the internet. Instead of buying hardware, users can rent these resources as needed. Businesses only pay for what they use and don’t have to worry about upgrades or maintenance. This pay-as-you-go model scales resources up or down based on demand.
For example:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2 – Cloud-based virtual servers.
- Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines – Scalable compute resources.
- Google Compute Engine – Pay-as-you-go virtual machine hosting
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
This approach lets developers build custom applications without dealing with physical hardware. Third-party providers offer the required tools and software for a simpler and faster development process.
For example:
- Google App Engine – Build and host apps with no infrastructure management.
- Microsoft Azure App Services – Simplifies app development and deployment.
- Heroku – Cloud platform for deploying web applications
Software as a Service (SaaS)
In this model, the provider manages everything for the user. There’s no need to download or install anything, and no technical skills are required. Users only need an internet connection and a browser to access the services and tools required on any device, like a computer, smartphone, or tablet.
For example:
- Dropbox – Cloud storage and file sharing.
- Salesforce – CRM software for sales and customer management.
- Zoom – Video conferencing and collaboration tools.
Top Cloud-Based Ideas to Chase
Gaming as a Service (GaaS)
Gaming as a Service (GaaS) or cloud gaming is a cloud-based system where users can play video games without needing expensive consoles or powerful hardware. Instead of installing games, players stream them online from remote servers.
Benefits:
- Lower Costs: Gamers can play high-quality games without buying costly equipment.
- Anytime Access: Games are available anywhere with a stable internet connection.
- Easy for Developers: Developers can update and improve games without interruptions.
- Better Gameplay: GaaS supports features like cross-platform play and advanced graphics.
Cloud-Powered Telemedicine Platform
A cloud-powered telemedicine platform uses cloud technology to make healthcare available from anywhere, connecting doctors, patients, and healthcare providers to communicate, share medical data securely, and work together in real-time without needing physical visits.
Benefits:
- Remote Consultations: Patients can talk to doctors from home, saving time and avoiding travel.
- Secure Health Records: Medical data is stored safely in the cloud and can be quickly accessed by patients and doctors.
- Scalability: These platforms can handle more users or services as healthcare needs grow.
- AI-Powered Insights: AI tools help with better diagnosis and personalized treatment.
- Cross-Device Access: Patients and doctors can use the platform on smartphones, tablets, or computers.
Energy-optimized Cloud Computing
Energy-optimized cloud Computing reduces the energy consumption of cloud systems, making them cost-effective and environmentally friendly. It uses smart technologies to lower the carbon effect of data centres while maintaining high performance.
Benefits:
- Lower Costs: Businesses save money by reducing energy use.
- Environmental Impact: Less energy consumption helps create greener operations.
- Regulatory Compliance: It helps organizations meet energy-use regulations.
- Efficient Design: Smart infrastructure focuses on saving energy and reducing waste.
- Resource Optimization: Techniques like virtualization and containerization improve resource use and cut energy waste.
- Renewable Energy Use: Cloud systems often integrate renewable energy sources for a cleaner approach.
- Competitive Edge: Companies focusing on energy efficiency stand out in the market.
- Sustainable Growth: Energy optimization supports the growing demand for cloud services without losing a lot of resources.
DevOps Automation and Infrastructure-as-Code
DevOps Automation and Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) combine software development and IT operations to simplify workflows and reduce errors. With IaC, cloud infrastructure is managed through code, automating tasks like setup and configuration.
Benefits:
- Code-Based Management: Infrastructure is created and managed using scripts, ensuring consistency and speed.
- Faster Delivery (CI/CD): Continuous integration and delivery automate testing and deployment for quicker software releases.
- Scalability and Reuse: Infrastructure can easily scale up or down, and configurations can be reused for multiple projects.
- Automated Monitoring: Systems constantly monitor performance and automatically handle recovery when issues occur.
- Version Control: Infrastructure changes are tracked like software code, improving transparency and reducing mistakes.
- Cost Savings: Automation reduces manual work and improves resource usage, lowering overall costs.
- Fewer Errors: Automating processes removes human error, leading to more reliable systems.
- Supports Cloud Systems: DevOps and IaC are key for managing modern, flexible cloud-based environments.

Edge Computing and IoT Integration
Edge Computing processes data closer to the location from where it is created rather than using a faraway cloud server to improve speed, reduce delays, and enhance performance, especially in real-time applications like smart cities and factory automation.
Benefits:
- Lower Latency: Processing data near its source reduces delays, improving response times.
- Better Bandwidth Use: Less data needs to be sent to the cloud, freeing up bandwidth for other tasks.
- Real-Time Decisions: Faster data processing enables immediate decisions, which is crucial for systems like self-driving cars and automated factories.
Virtual Reality (VR) Therapy
Virtual Reality (VR) Therapy uses immersive VR experiences to treat mental health, manage pain, and support rehabilitation. Cloud computing allows VR content to be delivered remotely to make it more accessible for patients and healthcare providers.
Benefits:
- Scalable Content Delivery: Cloud technology makes it easy to deliver VR therapy to many users, no matter where they are.
- Data Storage: Cloud storage keeps patient data, VR content, and progress secure and easy to access.
- Remote Access: Patients can access therapy from anywhere, making it more convenient and expanding its reach.
Real-Time Translation Services
Real-time Translation Services use AI and machine learning to instantly translate spoken or written languages. Cloud computing provides the power needed for fast processing and facilitates people to access these services worldwide.
Benefits:
- Global Access: Cloud technology lets users access translation services from anywhere, removing language barriers.
- Scalability: Cloud platforms can handle many translation requests at once, meeting the needs of users and businesses.
- Improved Accuracy: AI and machine learning algorithms in the cloud enhance translations over time by understanding context better.
Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) allows businesses to create and host blockchain applications without dealing with complex infrastructure. It provides a secure and decentralized ledger for storing and verifying transactions, making it perfect for industries like finance, healthcare, and logistics.
Benefits:
- Security: BaaS uses a decentralized system to securely manage transactions, reducing the chances of fraud or data breaches.
- Scalability: Cloud-based BaaS platforms can handle more transactions as businesses grow without losing performance.
- Flexibility: Businesses can customize blockchain applications for specific tasks like tracking transactions, managing supply chains, or ensuring secure communication.
Cloud Cybersecurity
Cloud Cybersecurity protects cloud-based systems, applications, and data from online threats. As businesses increasingly use the cloud, securing sensitive information has become essential. Cloud providers provide services like threat detection, identity management, and encryption to create a secure environment.
Benefits:
- Scalability: Cloud security solutions adjust to your growing data and infrastructure needs.
- Centralized Security: Security tools and processes are managed in one place, making monitoring and control easier.
- Real-Time Threat Detection: Advanced systems monitor continuously, helping businesses detect and respond to threats quickly to prevent data loss or breaches.
FinOps for Cloud Cost Management
FinOps (Financial Operations) combines finance, technology, and cloud operations to manage and optimize cloud costs. It helps businesses track spending, reduce unnecessary expenses, and ensure resources are used effectively.
Benefits:
- Cost Transparency: FinOps gives businesses a clear view of cloud spending, showing where and how resources are used.
- Optimization: It identifies opportunities to reduce costs while maintaining performance.
- Collaboration: FinOps encourages teamwork between finance, IT, and operations, ensuring everyone works together to control cloud costs and improve financial results.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is the backbone of innovation for businesses today. From cloud gaming and telemedicine to smarter supply chains and energy-efficient solutions, the opportunities are endless. Whether you’re looking to solve everyday problems, cut costs, or create something game-changing, cloud technology gives you the tools to make it happen. The future belongs to businesses that embrace the cloud and turn those ideas into reality.